Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter: Are you looking for the dual nature of radiation and matter? Then you are on the right page for more information about it. It is a property of matter is explained in terms of its particle nature. Further details are listed for the candidate’s reference purpose.
Therefore, wave-particle duality is an essential concept in quantum mechanics, which explains that every particle, or more precisely, a quantum entity, can be expressed as either a particle or a wave. This concept further helps to correct the inability of the theories of classical mechanics to explain the mechanism or behavior of matter.
Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter
Photoelectric Effect
The phenomenon of photoelectron emission from the surface of a metal when a light beam of appropriate frequency is incident on it.is called the photoelectric effect. The electrons emitted are called photoelectrons, and the electricity thus produced is called photoelectric current.
Hertz’s Observation, This phenomenon of photoelectric emission was discovered in 1887 by Heinrich Hertz in his electromagnetic wave experiment. His experimental research on generating electromagnetic waves by a spark in a detector loop.
Lennard’s Observation Lennard observed that when ultraviolet radiation is allowed to fall on the emitter plate of an evacuated glass tube surrounded by two electrodes, a current flows. As soon as the ultraviolet rays stopped, the current flows also stopped. These observations suggest that when ultraviolet rays fall on the emitter plate, electrons from it are attracted to the positive plate by the electric field.
There are several terms related to photoelectric effects, such as:
(i) Free electrons In metals, these electrons in the outer shells are loosely bound to the atoms, so they can quickly move within the metal surface but cannot leave the metal surface. Such electrons are called free electrons.
(ii) Electron emission The phenomenon of emission is electrons from a metal surface is called electron emission.
(iii) Photoelectric emission is the phenomenon of emission of electrons from a metal surface by light radiations of appropriate frequency.
(iv) Work function The minimum energy required to eject an electron from the outer surface of the metal is called the work function.
(v) Cutoff potential For a particular frequency of incident of radiation, the minimum negative (retarding) potential V0 given to the plate at which the photoelectric current becomes zero is called the cutoff or stopping potential.
(vi) Cutoff frequency The minimum frequency of light at which photoelectrons are emitted from a material is called threshold frequency or the cutoff frequency of that material.
(vii) Cutoff wavelength The maximum wavelength of light at which photoelectrons are emitted from a material is called the threshold wavelength or the cutoff wavelength of that material.
Effect of Light Intensity on Photocurrent For a fixed frequency of incident radiation, the photoelectric current increases linearly with the increasing intensity of incident light.
Effect of Potential is Photoelectric Current For a constant frequency and intensity of incident light, the photoelectric current increases with the potential applied to the collector. When all the photoelectrons reach plate A, the current becomes maximum, called saturation current.
EFFECT OF FREQUENCY OF INCIDENT RADIATION OF STOPPING PROBABILITY We take radiations of different frequencies but the same intensity. For each radiation, we will understand the variation of the photoelectric current against the potential difference between the plates.
Laws of Photoelectric Emission:
(i) For a given material and frequency of incident radiation, the photoelectric current of photoelectrons emitted per sec is directly proportional to the intensity of incident light.
(ii) Given the material and frequency of incident radiation, the saturation current is proportional to the intensity of incident radiation, while the stopping potential is independent of its intensity.
(iii) For a given material, there is one specific minimum frequency of incident radiation at which the emission of photoelectrons does not occur. This frequency is called threshold frequency. The threshold frequency, the maximum kinetic energy or equivalent stopping potential of the emitted photoelectron, is independent of the intensity of the incident light but depends only on the incident light’s frequency (or wavelength).
(iv) Photoelectric emission is a quick process. The time between the incidence of radiation and the emission of photoelectrons is less than 10-9 seconds.
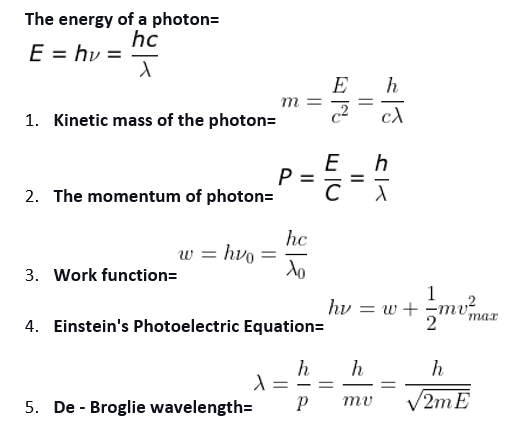
Einstein Photoelectric Equation, here Kmax = HV – Ф0 Where, hv = energy of the photon and Ф = work-function.
Conclusion:
De Broglie proved the dual nature of radiation and matter, confirmed by many experiments, including the David and Germer experiments. It is one of the most extensive experiments ever conducted on radiation and the nature of matter.
The dual nature has solved many theories and explained many concepts. In the presence of light emission by electrons, the dual nature of radiation is considered as wave nature and particle nature.
Examdays Article Agenda